Phase 2B in MTX-naïve RA patients with severe disease activity (finalized)
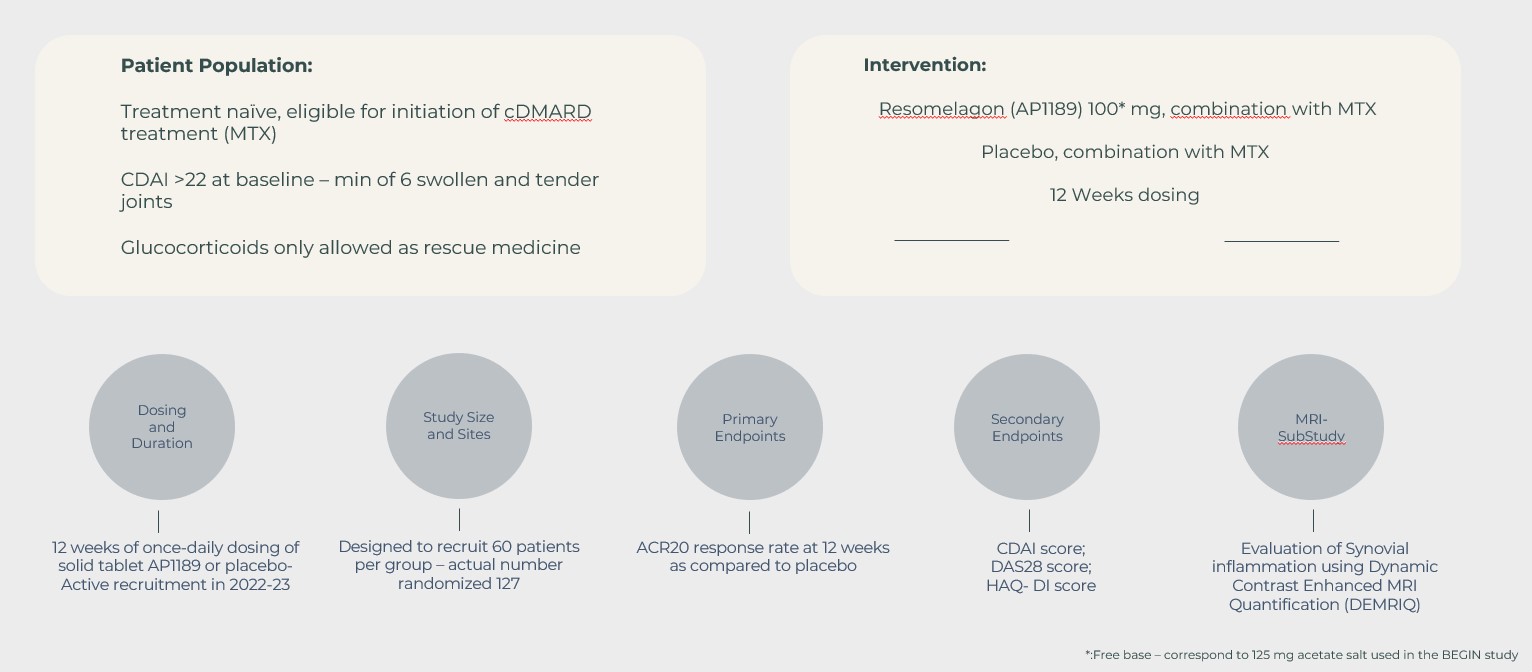
In continuation of the BEGIN study, the EXPAND study was designed to investigate the safety and disease activity (measured by the ACR20 response rate and other RA disease measures) following 12-weeks of treatment with a once daily 100 mg resomelagon tablet plus MTX compared to placebo plus MTX.
Resomelagon was safe and well tolerated. Similar incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were seen across treatment groups (44.4% and 42.2%). TEAEs were seen in 11.1% and 6.3% in the resomelagon vs placebo groups, respectively and included upper respiratory tract infections (6.3% vs 6.3%), abdominal pain upper (6.3% vs 3.1%), nausea (6.3% vs 3.1%), and headache (0% vs 9.4%), resomelagon vs placebo respectively. Two serious TEAEs were reported; one in the resomelagon group and one in the placebo group but both were unrelated to study drug. Six subjects reported TEAEs leading to discontinuation; five in the resomelagon group (3 subjects with drug-related gastrointestinal disorders); and one in the placebo group (unrelated to study drug).
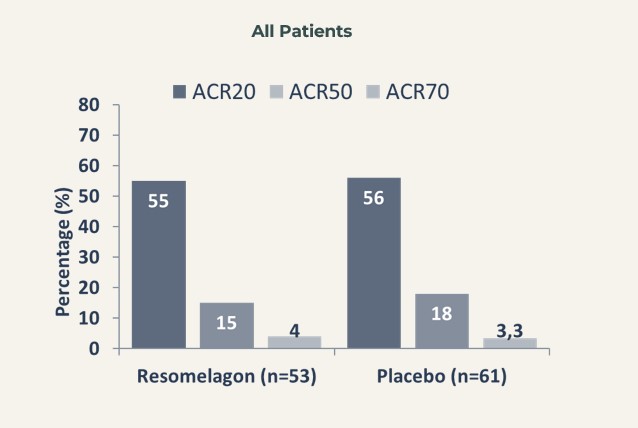
No statistically significant difference was obtained between resomelagon and placebo in the ACR20 response rate at week 12 (54.7% and 55.7% in the resomelagon and placebo groups, respectively) – meaning that the primary endpoint of the study was not met.
However, of the patient population in the EXPAND study around 40% did not show signs of systemic inflammation, as high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) were in the normal range (ie hsCRP <3 mg/L). Further, a fraction of the patients was not considered newly diagnosed with some being without adequate treatment for years before entering into the study. Therefore, these patients should probably not have been included in the study.
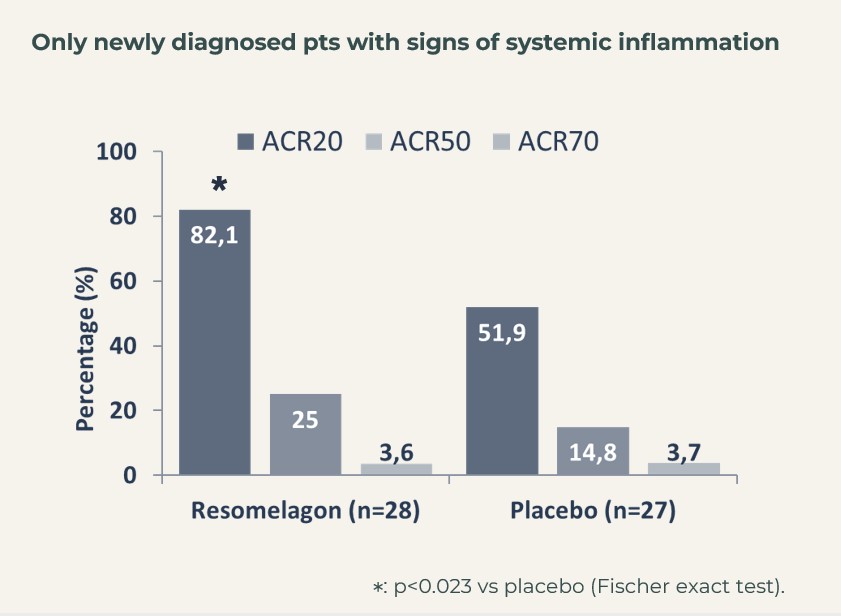
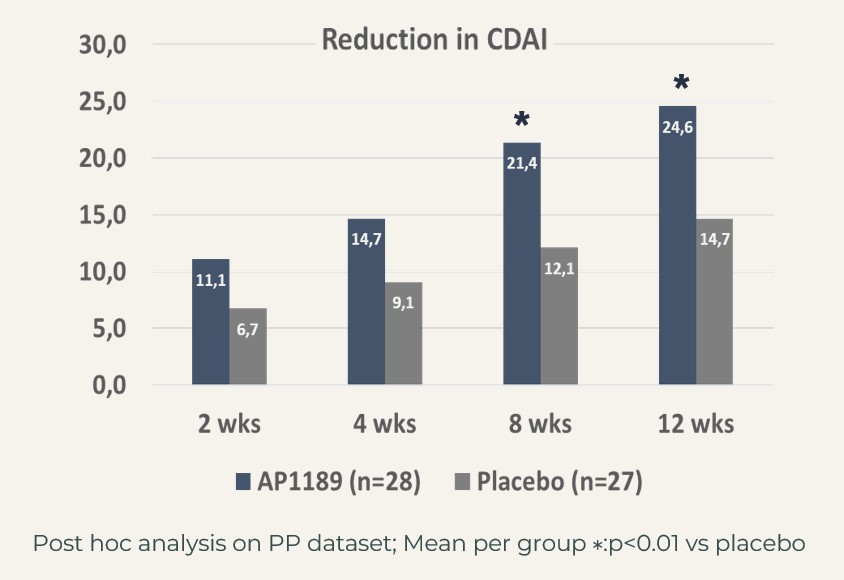
When focusing of the segment of patients, that were considered newly diagnosed (defined as having been diagnosed with RA within 6 months of inclusion into the study) and who showed signs of systemic inflammation (hsCRP>3 mg/L at introduction to the study), ACR20 actually reached 82% in the resomelagon group (n=28) vs 52% in the placebo group (n=27), p<0.05 using Fisher’s exact test.
The treatment effect in this very relevant patient segment, mimicking the patients in the BEGIN study, i.e. to be considered the target population for resomelagon in RA was further supported by significantly larger reduction in disease activity measures:
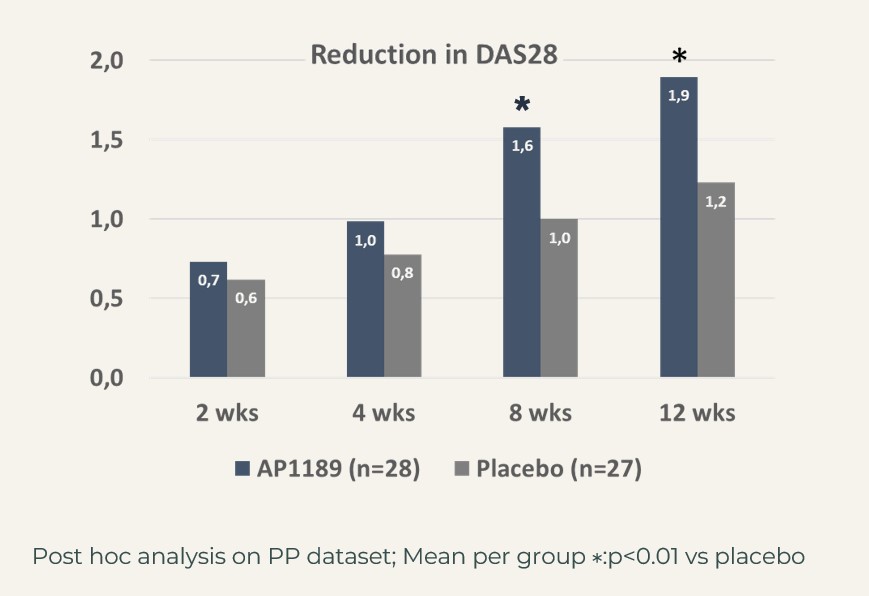
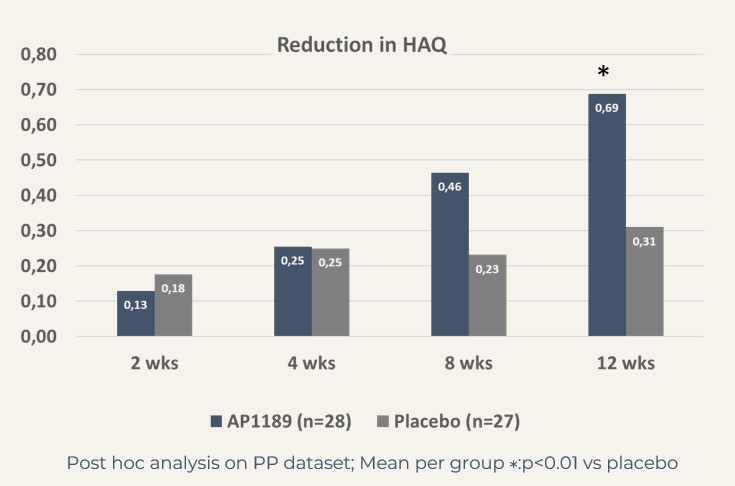
CDAI: resomelagon (n=28): 24.6 points vs placebo (n=27): 14.7 points, p<0.01; DAS28-CRP: resomelagon (n=28): 1.9 points vs placebo (n=27): 1.2 points, p<0.01. Also, the improvement in health assessment questionnaire HAQ), a measure of the patient’s ability to handle daily living was significantly larger in the resomelagon group: change in HAQ: resomelagon (n=28): 0.69 points vs placebo (n=27): 0.31 points, p<0.05.
Together these above post-hoc analyses strongly support further development of resomelagon in newly diagnosed RA patients with high disease activity including signs of systemic inflammation treated together with MTX.